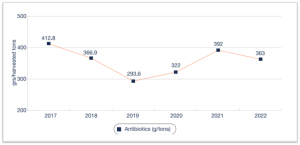
The big amount use of antibiotics in salmon farming is a very serious problem throughout the world, especially in Chile. In order to get a better fish quality, it is necessary to reduce the use of antibiotics.
Reducing the use of antibiotics in salmon farming is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Improve Farming Conditions
- Water Quality Management: Maintaining clean water is crucial for disease prevention. Regularly monitor water for harmful substances and ensure sufficient oxygen levels.
- Stock Density Control: Managing the density of fish in farms helps reduce contact between individuals, thereby minimizing the spread of disease.
- Feed Management: Providing high-quality, nutritionally balanced feed can strengthen the immune systems of salmon, making them less susceptible to diseases.
- Use copper alloy net: Taking the advantage of anti biological adhesion of copper, the copper alloy net can increase the water flow rate and oxigen rate, provide better living condition for the fishes.
2. Use Vaccinations
- Vaccination: Administering vaccines against common pathogens can significantly reduce the incidence of diseases, lowering the need for antibiotics.
3. Biological Control Methods
- Probiotics: Adding probiotics to feed helps establish and maintain a healthy gut microbiota, enhancing the salmon’s natural immunity.
- Natural Antimicrobials: Utilizing natural antimicrobial agents, such as plant extracts or seaweed, can inhibit the growth of pathogens.
4. Disease Monitoring and Early Diagnosis
- Regular Health Checks: Conduct regular health assessments and disease monitoring to detect and address potential health issues early, reducing the likelihood of outbreaks.
- Advanced Monitoring Technologies: Implement smart sensors and data analysis tools to continuously monitor the farming environment and fish health, allowing for timely preventive actions.
5. Integrated Management Approaches
- Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA): Co-cultivating salmon with other species, such as shellfish and seaweed, can create a more balanced ecosystem, reducing the incidence of disease.
- Selective Breeding: Breeding salmon with greater disease resistance can help lower the occurrence of illnesses and the reliance on antibiotics.

By implementing these strategies, it’s possible to effectively reduce the use of antibiotics in salmon farming, leading to healthier and more sustainable aquaculture practices.

